
python Sum of Nested Lists for each key in dictionary Stack Overflow
To sum a list of numbers: sum (list_of_nums) Generate a new list with adjacent elements averaged in xs using a list comprehension: [ (x + y) / 2 for x, y in zip (xs, xs [1:])] Sum all those adjacent elements into a single value: sum ( (x + y) / 2 for x, y in zip (xs, xs [1:]))
Ways To Iterate Through List In Python Askpython Riset
Example 1: Sum of numbers in a list. To sum the numbers in a list in Python from the initial value to the final, you can use the following code: numbers = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] total = sum (numbers) print (total) In this example, sum () function is used to add all numbers in the list. The output will be 150 as the total of all numbers in the.
Tableta Strom Zvyklí python add all elements of a list Oplatka Den
1.2 Overview of the sum() Method. One common operation you might need to perform on a list is calculating the sum of its elements. Python provides a built-in function called sum() that does just that.. The sum() method is designed to work with iterable objects like lists and takes a sequence of numbers as input, returning the sum of its elements. In this beginner's guide, we'll explore the sum.

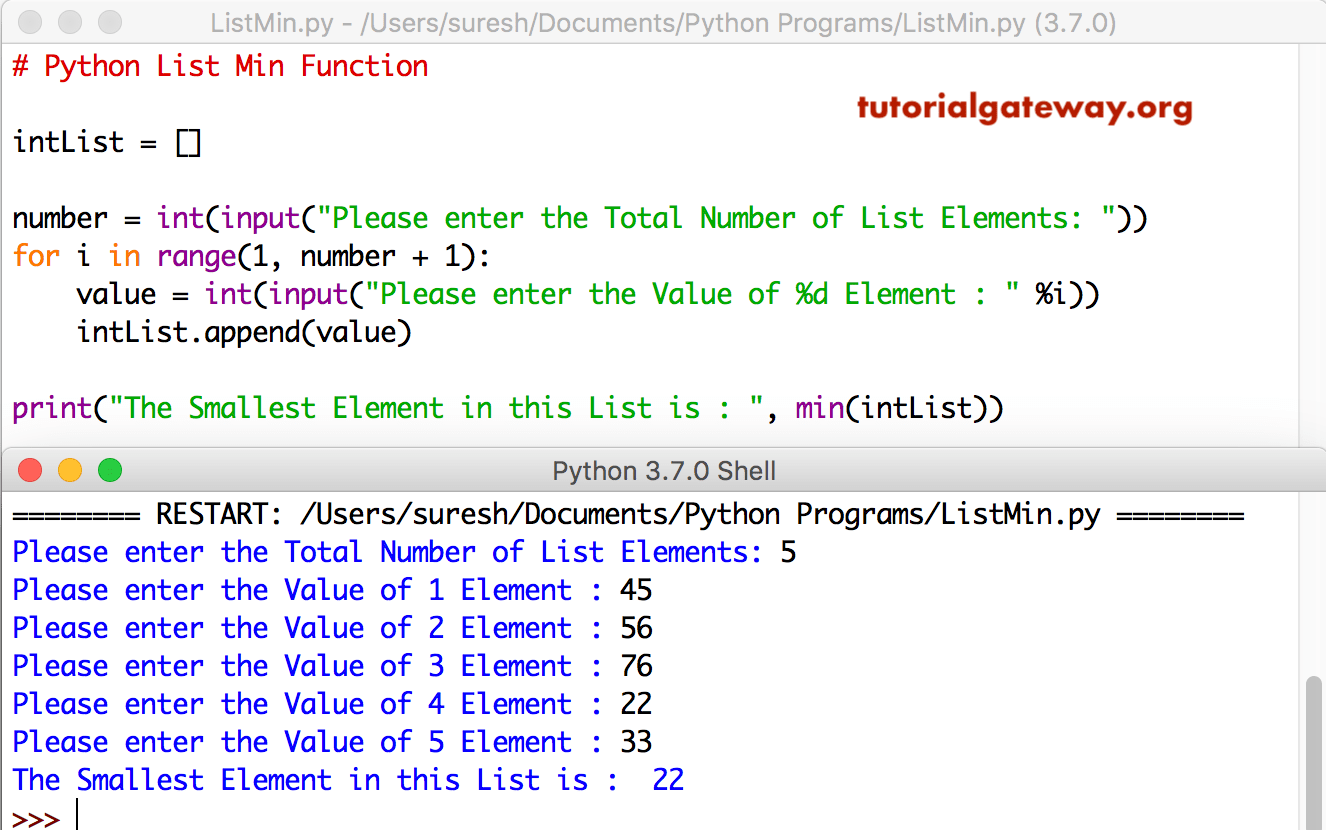
How to Find the Minimum of a List of Lists in Python? Be on the Right
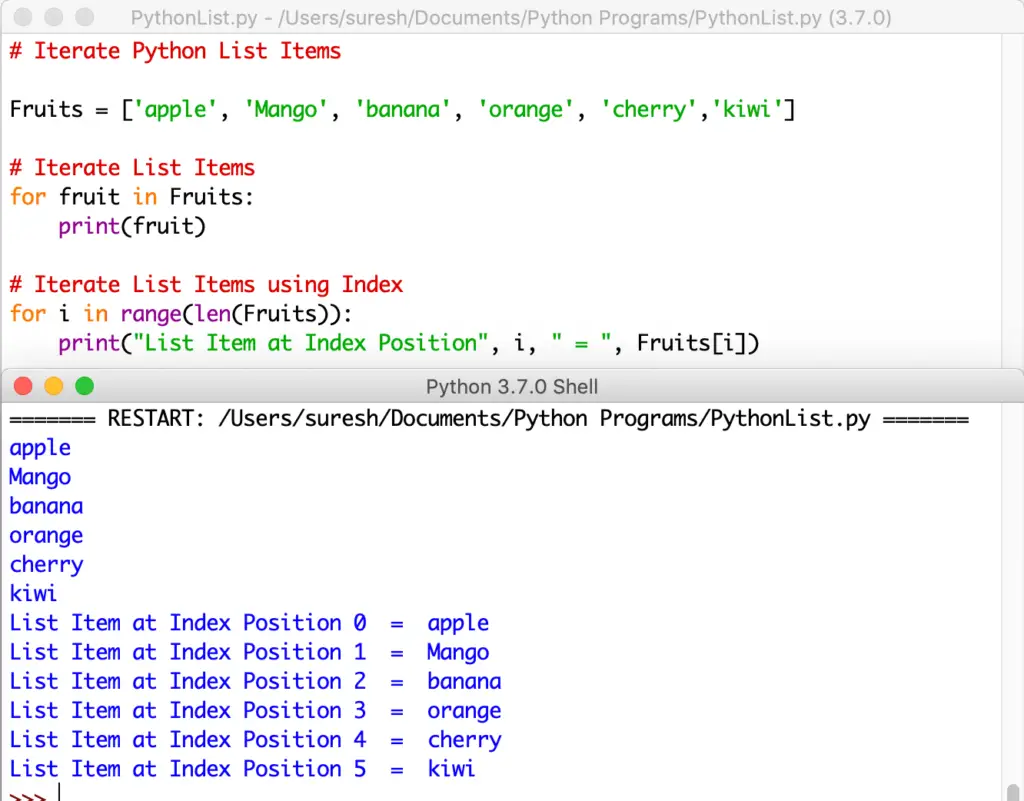
Lists in Python. A list is a data structure in Python that is used to store a collection of items. Lists are mutable, which means that their content can be changed. Lists can contain elements of different data types such as integers, strings, or even other lists. Finding the Sum of All Elements in a List in Python

Python One Line Sum List Be on the Right Side of Change
result = map (sum, a) Is the way I would do it. Alternatively: result = [sum (b) for b in a] The second variation is the same as yours, except it avoids the unnecessary range statement. In Python, you can iterate over lists directly without having to keep a separate variable as an index. Share. Improve this answer.

How to Sum List of Lists in Python? [Rows] Be on the Right Side of Change
Python's built-in function sum () is an efficient and Pythonic way to sum a list of numeric values. Adding several numbers together is a common intermediate step in many computations, so sum () is a pretty handy tool for a Python programmer. As an additional and interesting use case, you can concatenate lists and tuples using sum (), which.

How to Add Two Lists Element into One List in Python Addition of Two
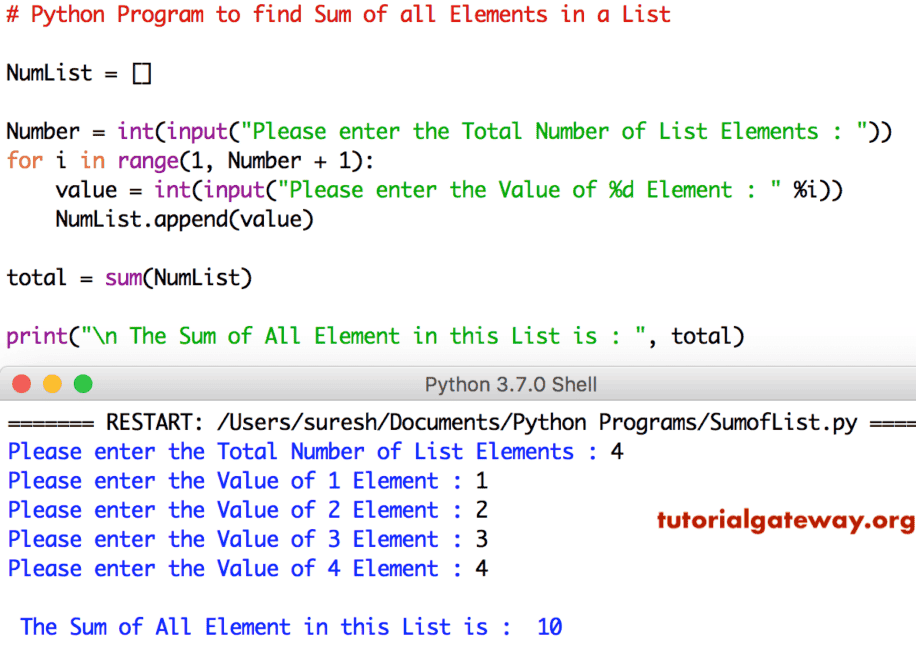
Python lists are one of the most used data structures. We often need to perform different operations on lists. In this article, we will discuss different ways to find the sum of elements in a list in python. Find Sum Of Elements In A List Using For Loop
Python Program To Find Sum And Average Of N Natural Numbers Gambaran
The simplest way to find the sum of a list in Python is by using the built-in sum () function. For example, Suppose we have a list of the tallest buildings in New York City, measured in feet: Here, the sum () function computes the total height of the tallest buildings in New York City. The function accepts an iterable (like our list) and adds.
Python min List Function
Here is my code, I need to sum an undefined number of elements in the list. How to do this? l = raw_input() l = l.split(' ') l.pop(0) My input: 3 5 4 9 After input I delete first element via l.pop(0). After .split(' ') my list is ['5', '4', '9'] and I need to sum all elements in this list. In this case the sum is 18.

Python List of Lists A Helpful Illustrated Guide to Nested Lists in
Method 1: Using the sum () function. To calculate the sum of the list in Python, you can use the "sum ()" function. The built-in sum () function is an efficient and Pythonic way to sum a list of numeric values. To add floating-point numbers with exact precision, use the fsum (iterable) instead. Loaded 0%.
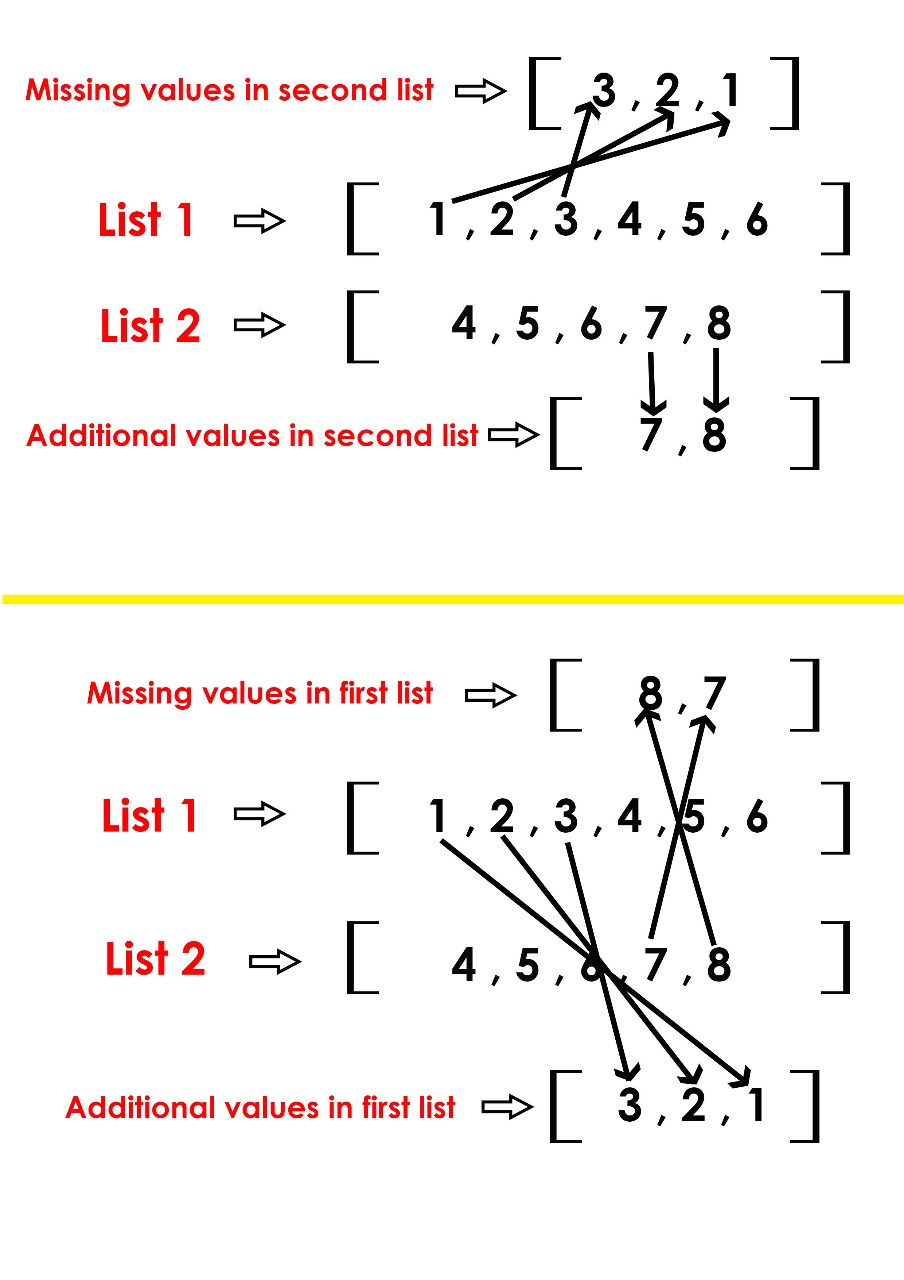
Python Find missing and additional values in two lists
The Basic Approach: Using the Built-in Sum Function. Python provides a built-in function, sum(), specifically designed to add up all the numbers in a list. This function takes a list as its argument and returns the sum of the items in the list. Here is an example of how to use the sum() function:

How to find number of elements in a list in Python? Python, List, Numbers
The sum in Python with For Loop. In this, the code first defines a list of numbers. It then initializes a variable called total to 0. The code then iterates through the list using a for loop, and for each number in the list, it adds that number to the total variable. Finally, the code prints the total value, which is the sum of the numbers in.

How to Sum Elements of Two Lists in Python Comprehensions and More
sum list elements using for loop. The first two examples will traverse through the entire list using a for loop. Meanwhile, every single value is added to the total variable. As a result, the sum of the entire list is returned at the end. Example 1: sum list elements using for loop
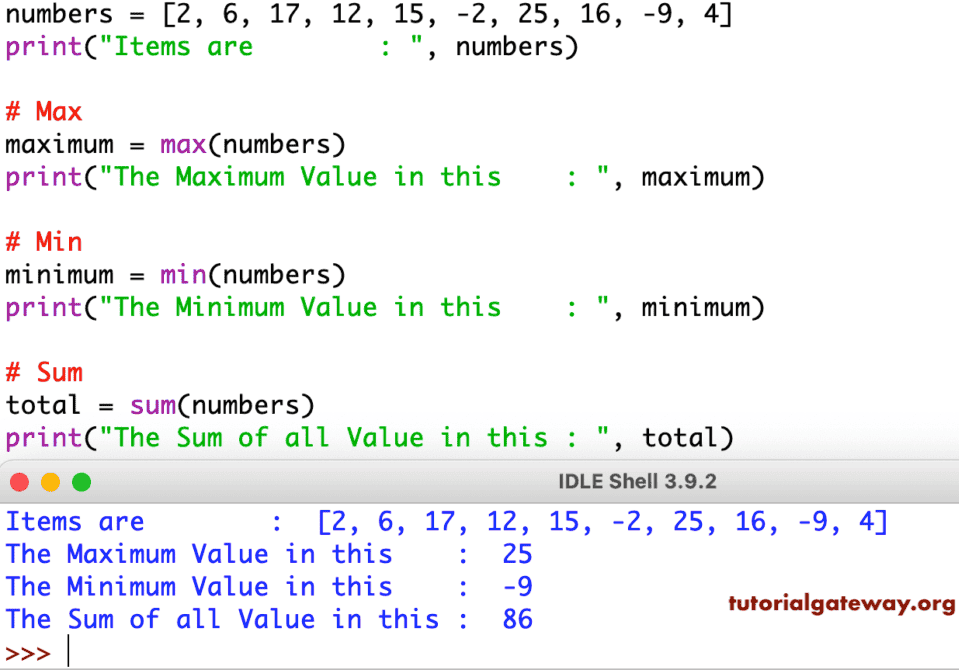
Python List Functions
Python Sum List Ignore None. Problem: Given is a list of numerical values that may contain some values None. How to sum over all values that are not the value None? Example: Say, you've got the list lst = [5, None, None, 8, 12, None, 2, 1, None, 3] and you want to sum over all values that are not None.

Python Lists YouTube
To get the sum total of a list of numbers, you can pass the list as an argument to the sum () function. # create a list. ls = [10, 15, 20, 25] # sum of list elements. sum(ls) Output: 70. We get the sum of the values in the list as a scaler value. Note that the sum () function may result in loss of precision with extended sums of floating-point.
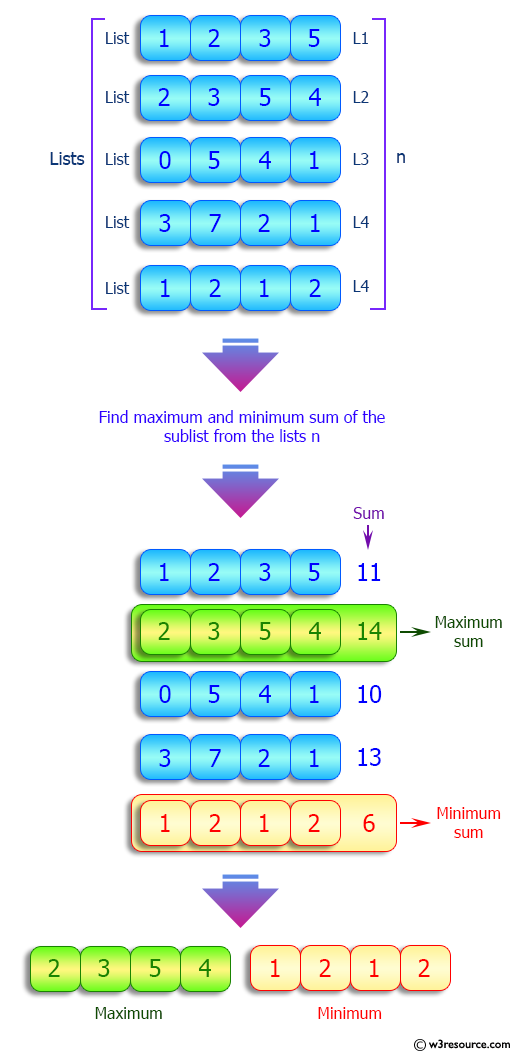
Python Calculate the maximum and minimum sum of a sublist in a given
Sum of Elements in a List in Python: A tutorial on SparkByExamples that showcases different methods to compute the sum of elements in a list using Python. Conclusion: Summing Python Iterables We've journeyed through the various ways to calculate the sum of a Python list, each with its unique strengths and considerations.